Dropsa
Dropsa
Lubrication Systems Solutions Specialists
- Accueil
- Société
- Solutions
 Pour Secteurs Industriels
Pour Secteurs Industriels- Machines agricoles
- Énergie
- Cimenteries et matières premières
- Industrie alimentaire et des boissons
- Machines-outils, presses et formage de métaux
- Sawing machines
- Presses
- Marine et Offshore
- Industrie minière et génie civil
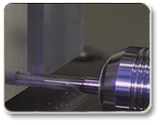 MQL: Usinage à Sec
MQL: Usinage à Sec Autres applications spéciales
Autres applications spéciales- Papier et bois
 Chemins de fer
Chemins de fer- Acier et aluminium
 Transport-Équipement et Infrastructure
Transport-Équipement et Infrastructure Textiles
Textiles
 Pour Lubrification
Pour Lubrification
- Pour études de cas
 CATALOGUE COMPOSANTS
CATALOGUE COMPOSANTS Pompes
Pompes Répartiteurs
Répartiteurs Restricteurs et injecteurs
Restricteurs et injecteurs Distributeurs
Distributeurs Raccords
Raccords  Tuyaux rigides, flexibles et outils
Tuyaux rigides, flexibles et outils Contrôleurs
Contrôleurs- MQL - Lubrification en Quantité Minimale
 Lubrification air huile
Lubrification air huile Systèmes de Pulvérisation
Systèmes de Pulvérisation Produits spéciaux
Produits spéciaux Valves
Valves Pulvérisateurs et buses
Pulvérisateurs et buses Brosses
Brosses Filtres
Filtres Réservoirs
Réservoirs Accessoires
Accessoires Lubrifiants et produits consommables
Lubrifiants et produits consommables Sondes et dispositifs de surveillance
Sondes et dispositifs de surveillance
- Formulaire de contact
- Blog