Dropsa
Dropsa
Lubrication Systems Solutions Specialists
- Home
- About Dropsa
- Lubrication Solutions
 Lubrication Solutions by industry
Lubrication Solutions by industry- Agricultural machinery
- Energy and Utilities
- Cement factories and raw materials
- Food and beverage
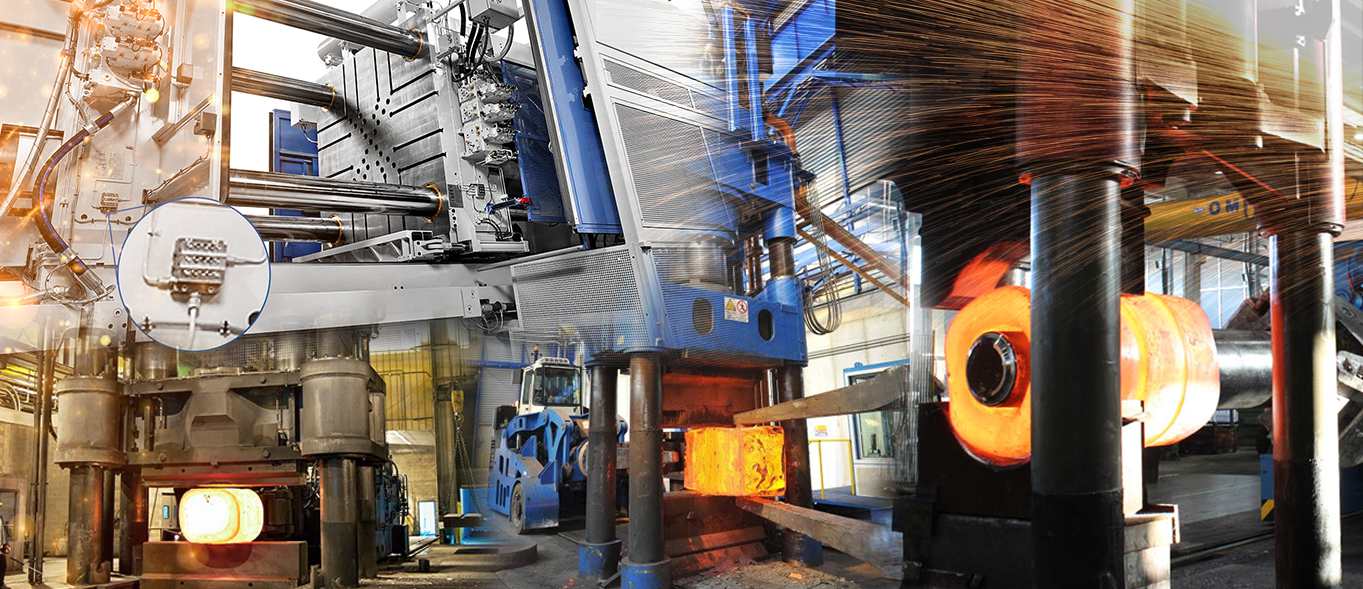
- Machine tools and metal forming
- Sawing machines
- Presses
- Marine & Offshore
- Mining and construction
 MQL: Near Dry Machining
MQL: Near Dry Machining Other-special application
Other-special application- Paper and wood
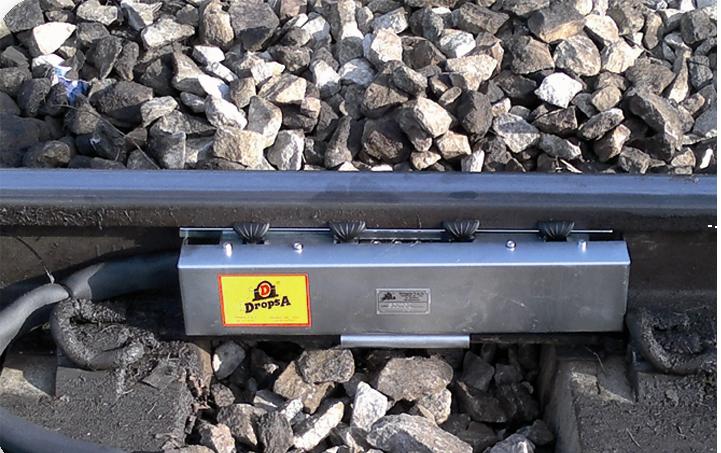 Railways
Railways- Steel and aluminium
 Transport- Equipment and Infrastructure
Transport- Equipment and Infrastructure Textiles
Textiles
 By Lubrication Type
By Lubrication Type
- BY CASE STUDY
 COMPONENT CATALOGUE
COMPONENT CATALOGUE
- Contact us
- DropsA Companies
- Find your nearest Distributor
- TRIBOTEC
- EREDI DI MAURO FARINA SRL
- DropsA GmbH (Germany)
- BIBUS Austria Ges. m. b. H.
- TOYO
- EUROSCALE MOBLITECHNIKA KFT
- TRIBOTEC
- Układy Centralnego Smarowania Sp. z o.o.
- Equinotec
- SC PROCONS SRL
- Transcendo Solutions Global Inc.
- HIDROPRES
- MOTORIMPEX LTD
- B-Fluid
- I.M.T. Srl
- M.T. TECNOLOGIE SRL
- Bianchi Industrial SpA
- Hidrotecnica srl
- ATI srl Articoli Tecnici Industriali
- ROMANA AUTOMAZIONI
- Comes - industrial Construction Partner
- FROST ENGINEERING SERVICE
- Custom Fluid Power
- DropsA Do Brasil
- IMPORTADORA LA ESTRELLA LTDA
- WINDLUB AUTO SERVICE
- PEO TECH Co. Ltd.
- OCEAN POWER INTERNATIONAL LLC
- THAISON INDUSTRIAL COMPANY LTD COPY -
- JADIFLEX
- DropsA Spicelube India Pvt Ltd.
- DropsA Lubrication Systems (Shanghai) Co., LTD
- DropsA Australia Pty Ltd
- Tiberium Trading
- ARIA COMPRESSA
- HYDROSCAND
- PT. CELEBES NUSANTARA
- Guang zhou Hyetone Mechanical & Electrical Equipment Co.,Ltd
- Partner Classification
- Feedback & Customer Satisfaction
- Blog